만성 부비동염, Chronic paranasal sinusitis
- 다음 정보를 참조(Please visit the following article) www.drleepediatrics.com-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 제 2부 신체각계통 별 응급의료 제17장: 소아청소년 이비인후 질환 응급의료 참조
- Please visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System-Chapter 17: Pediatrics Ear, Nose.
- Throat, larynx Disease Emergency Medical Reference
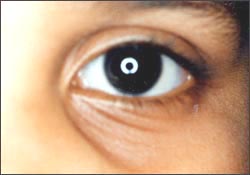
사진 115. 만성 부비동염은 세균 감염으로도 생길 수 있고 알레르기로도 생길 수 있다. 알레르기성 부비동염이 있을 때는 알레르기성 샤이너가 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
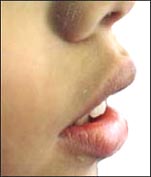
사진 116. 알레르기성 비염과 알레르기성 부비동염이 있을 때는 입을 벌리고 숨을 쉬는 경구호흡도 하고, 상하악 치열이 서로 맞지 않아 부정교합이 생길 수 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
- 급성 부비동염을 적기에 적절히 치료하지 않아서 급성 부비동염이 완전히 낫지 않고 2~3개월 이상 오랫동안 계속될 때 만성 부비동염이 생길 수 있다. 또는 부비동염의 증상이 4주 이상 계속 될 때 만성 부비동염이라고도 한다.
만성 부비동염의 원인
- 폐렴연쇄상구균, 헤모필러스인플루엔자균, 또는 모락셀라균 등 박테리아가 부비동 속에 감염되어 급성 부비동염을 일으킬 수 있다(표 1 참조).
- 급성 부비동염을 적절히 치료하지 않으면 급성 부비동염이 만성 부비동염으로 이어질 수 있다.
- 박테리아 만성 부비동염만 있을 때도 있다. 그러나 알레르기성 비염, 선천성 코 기형, 또는 다른 종류의 어떤 코 병이 있을 때 그 병과 같이 만성 부비동염이 있는 것이 보통이다.
- 선천성 코 기형이나 코 타박상으로 생긴 코 변형, 적절히 치료되지 않은 충치, 비강 내 물혹(폴립/비용/Polyps) 등이 있을 때 만성 부비동염이 함께 생길 수 있다.
만성 부비동염의 증상 징후
- 환아의 나이, 만성 부비동염을 일으킨 박테리아의 종류, 만성 부비동염을 앓을 때 같이 있는 병, 즉 동반 질병의 종류 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 맑은 콧물이 나올 수도 있고 고름과 같이 누렇거나 푸르스름한 콧물이 나올 수도 있다.
- 잘 때 콧물이 비강의 후부로 흘러 간 후 인두강 상부로 내려가기 때문에 밤에 자다가 기침을 조금 할 수 있다.
- 코가 자주 막혀 호흡곤란이 생길 수 있다.
- 만성 부비동염이 있는 부비동 부위가 아플 수 있고 머리가 아플 수 있다.
- 열은 거의 나지 않는다.
- 주의력 결핍 장애가 생겨 정신 집중을 잘 할 수 없고 공부하는 데 지장이 생길 수 있다.
- 전신 권태감이 생기고 자주 피로하다고 호소한다.
- 콧물이 자주 나고 코가 막히고 코로 숨쉬기 불편하다.
- 입을 벌리고 숨 쉬는 경우가 많다.
- 알레르기성 비염이 만성 부비동염과 함께 있을 때는 경구호흡을 한다.
- 아데노이드 얼굴형(아데노이드 안모)이 생길 수 있다.
- 알레르기성 비염 참조.
- 만성 부비동염이 있는 아이들은 기관지 천식, 아토피성 피부염, 알레르기성 비염 등 알레르기성 질환의 병력이 있는 경우가 많다. 사진 115에서 볼 수 있는 것 같이 알레르기(성) 샤이너가 생길 수 있다.
만성 부비동염의 진단
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합하고 부비동 X-선 사진, 부비동 CT 스캔 검사, 초음파 사진, 부비동 MRI 검사 등으로 진단할 수 있다.
- 비강 점액 호산구 검사를 해 진단하는데 도움을 받을 수 있다.
- 면역 결핍증, Wegener 병, 낭성섬유종 등 드문 콧병이나 비강 차단성 어떤 질병이 있나 확인하기 위해 CT 검사를 하고 이비인후과 전문의의 자문을 얻는다.
- 알레르기성 진균 비염, 면역 결핍증 등과 감별 진단한다.
만성 부비동염의 치료
- 환아의 나이, 원인, 합병증의 유무, 알레르기 질환 유무 등에 따라 치료한다.
- 대부분의 만성 부비동염은 항생제로 쉽게 치료 되지 않는다.
- 아목시실린이나 다른 종류의 적절한 항생제로 2~6주간 치료한다. 성인의 경우 3개월 간 마크로라이드(Macrolide) 항생제로 치료하기도 한다.
- 알레르기성 비염을 치료할 때는 알레르기성 비염도 동시 치료해야 하고, 충치로 생긴 만성 부비동염은 충치도 함께 치료해야 한다.
- 선천성 코 기형이나 후천성 코 변형이 있을 때는 그것도 적절히 치료해야 한다.
- 머리가 아프고 코가 자주 막히면, 페닐에프린제 코 분무나 페닐에프린제 코점적약, 또는 다른 종류의 비강 점막층 충혈 완화제 분무를 비강 속에 직접 뿌리거나 비강 속에 넣어 치료한다.
- 페닐에프린 코점적약제나 분무로 치료할 수 있다. 페닐에프린 코점적약제는 3~5일 이상 써서는 안 된다.
- 슈도에페드린제나 액티페드, 또는 다른 종류의 경구용 비강 점막 충혈 완화제로 치료 할 때 만성 부비동염의 증상 징후가 일시적으로 좋아질 수 있다.
- 콧구멍 속을 통해 비강 속에 뿌리는 베코나제 분무나 반세나제 분무 등 코르티코스테로이드제 소염제나 클로몰린 소염제 분무로 치료하면 만성 부비동염의 주원 알레르기성 비염도 잘 치료된다.
- 2세대 항히스타민제를 경구로 복용해 치료해 볼 수도 있고 코티코스테로이드 비강 분무제로 치료 할 수도 있다.
- 아주 드물게, 필요에 따라, 부비동 내에 괸 고름을 주사 바늘로 빼는 치료도 한다.
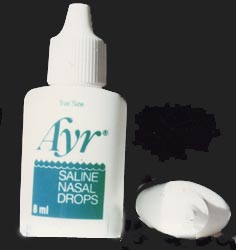
사진 117. 만성 부비동염을 생리 식염수 코 분무나 코 점적약제를 비강 내에 넣어 치료하기도 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Chronic paranasal sinusitis
• Please visit the following article: www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System See Chapter 17: Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescent Otolaryngology
• Please visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System-Chapter 17: Pediatrics Ear, Nose.
• Throat, larynx Disease Emergency Medical Reference

Picture 115. Chronic sinusitis can be caused by a bacterial infection or an allergy. If you have allergic sinusitis, you may develop allergic shiner. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP

Photo 116. When you have allergic rhinitis and allergic sinusitis, you can also breathe with your mouth open orally, and the upper and lower teeth do not match, so malocclusion may occur. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
• Chronic sinusitis may occur when acute sinusitis is not treated in a timely manner and the acute sinusitis does not completely heal and continues for more than 2-3 months. Or, when the symptoms of sinusitis last for more than 4 weeks, it is also called chronic sinusitis. Causes of chronic sinusitis
• Bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, or Moraxella can infect the sinuses and cause acute sinusitis (see Table 1).
• If acute sinusitis is not properly treated, acute sinusitis can lead to chronic sinusitis.
• Sometimes there is only bacterial chronic sinusitis. However, it is common to have chronic sinusitis, such as allergic rhinitis, congenital nasal malformation, or any other type of nasal disease.
• Chronic sinusitis can also occur when there are congenital nasal deformities or nasal deformities caused by nasal contusions, dental caries that are not properly treated, and nodules (polyps/costs/Polyps) in the nasal passages. Signs of symptoms of chronic sinusitis
• Symptoms differ depending on the child’s age, the type of bacteria that caused chronic sinusitis, and the type of comorbid disease that is present with chronic sinusitis.
• A clear runny nose may come out, or a runny nose that is yellow or bluish like pus may come out.
• When you sleep, runny nose flows down the back of the nasal passages and then down the upper pharyngeal cavity, so you may cough a little at night.
• Frequent stuffy nose can make breathing difficult.
• With chronic sinusitis, the sinus area may be sore and the head may hurt.
• Almost no heat.
• You may have Attention Deficit Disorder, which makes it difficult for you to concentrate and interfere with your studies.
• General malaise and frequent complaints of fatigue.
• Frequent runny nose, stuffy nose, and difficulty breathing through the nose.
• I often breathe with my mouth open.
• When allergic rhinitis coexists with chronic sinusitis, perform oral breathing.
• Adenoid face shape (adenoid face) may occur.
• See Allergic Rhinitis.
• Children with chronic sinusitis often have a history of allergic diseases such as bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis. As can be seen in photo 115, allergy (sex) shiner may occur. Diagnosis of chronic sinusitis
• The diagnosis can be made by synthesizing the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, and using sinus X-rays, sinus CT scans, ultrasonography, and sinus MRI scans.
• A nasal mucus eosinophil test can help with the diagnosis.
• Perform a CT scan and consult an otolaryngologist to check for any rare rhinorrhea or nasal obstruction such as immunodeficiency syndrome, Wegener’s disease, or cystic fibrosis.
• Differentially diagnose allergic fungal rhinitis and immunodeficiency syndrome. Treatment of chronic sinusitis
• Treatment depends on the child’s age, cause, presence of complications, and presence of allergic diseases.
• Most chronic sinusitis is not easily treated with antibiotics.
• Treat with amoxicillin or other appropriate antibiotics for 2-6 weeks. Adults are sometimes treated with macrolide antibiotics for 3 months.
• When treating allergic rhinitis, allergic rhinitis should be treated simultaneously, and chronic sinusitis caused by tooth decay should be treated together.
• If there is a congenital or acquired nasal deformity, it should be treated appropriately.
• If you have a headache and frequent nasal congestion, treat with phenylephrine nasal spray, phenylephrine nasal drops, or another type of nasal mucosal decongestant spray directly into or into the nasal passages.
• It can be treated with phenylephrine nasal drops or spray. Phenylephrine nasal drops should not be used for more than 3 to 5 days.
• Symptoms of chronic sinusitis may temporarily improve with treatment with pseudoephedrine, Actifed, or other oral nasal mucosal decongestants.
• Allergic rhinitis, the main cause of chronic sinusitis, can also be treated well if treated with corticosteroid anti-inflammatory agents or cromolyn anti-inflammatory sprays such as Beconase spray or Bansenase spray sprayed into the nasal passages through the nostrils. • Treatment may be attempted by taking second-generation antihistamines orally, or it may be treated with corticosteroid nasal sprays.
• In very rare cases, if necessary, a needle may be used to drain the pus from the sinus.

Photo 117. Chronic sinusitis is sometimes treated by injecting saline nasal spray or nasal drops into the nasal cavity. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
-
HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL, INFECTIOUS DISEASES IN PRIMARY CARE OCTOBER 14-16, 2015
-
그 외
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.