신생아 흡인 폐렴, Aspiration pneumonia in newborn infants
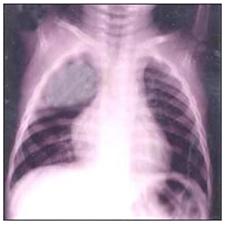
사진160.폐렴이 가슴 X선 사진
우측 폐의 상엽에 폐렴이 있다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
- 분만 전이나, 분만 중, 또는 분만 직후에 태아나 신생아가 양수, 모체가 흘린 피, 태변 등을 기도 속으로 흡인해서 생긴 폐렴을 신생아 흡인 폐렴, 또는 신생아 흡입성 폐렴이라고 한다.
| 신생아 흡인 폐렴의 원인 |
- 보통 이상으로 분만 시간이 오래 걸려서 태어난 신생아
- 양막이 터지고 시간이 많이 경과한 후에 분만하여 태어난 신생아
- 난산으로 태어 날 때
- 자궁내 태아가 산소 공급을 충분히 받지 못해서 양수 및 태변을 폐 속으로 흡입한 후 태어날 때
- 출생 이후 신생아 자신이 토한 위장 내용물이 기도 속으로 흡인됐을 때도 흡인 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 구토물을 기도 속으로 흡인될 때는 흡인물과 박테리아가 함께 폐 속으로 흡인돼서 폐 속으로 들어가게 된다. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환-늑막염과 농흉, 기흉 참조.
- ⑥ 그 외 다른 원인으로 갓 태어난 신생아에게 흡인 폐렴이 생길 수 있다. 제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환-흡인 폐렴 참조.
| 신생아 흡인 폐렴의 증상 징후 |

사진 161.흡인구 (Suction bulb).
비강, 입안, 인두강 등에 있는 태변, 피, 구토물 등을 흡인해서 기도가 열리게 하고 호흡을 잘 하도록 돕고 흡인 폐렴 등을 예방하는데 흡입구를 주로 쓴다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
사진 162.흡인 카테터
비강, 입안, 인두강 등에 있는 태변, 피, 구토물 등을 흡인해 기도가 열리게 하고 호흡을 잘 할 수 있게 도와주고 흡인 폐렴을 예방하는데 주로 쓴다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
- 하기도 속으로 흡입된 구토물, 피, 양수 등의 양과 흡인 폐렴의 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 조금씩 다를 수 있다.
- 심한 흡인 폐렴의 전형적인 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
- 숨이 가쁘고, 피부가 창백하거나 파랗다.
- 숨 쉴 때 신음소리를 내기도 한다.
- 박테리아 감염이 없고 흡인 폐렴만 있을 때는 열이 나지 않는 것이 보통이다.
- 흡인 폐렴에 박테리아 감염이 2차적으로 생겨 박테리아 폐렴이 동시 있을 때는 열이 날 수 있다.
- 젖이나 인공영양을 잘 빨아먹지 않는다.
- 이런 증상 징후가 며칠내지 1 주간 계속될 수 있다.
| 신생아 흡인 폐렴의 진단 치료 |
- 병력, 증상 징후, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 이 병이 의심되면 가슴 X선 사진 검사로 진단한다.
- 초기에는 박테리아 폐렴이나 바이러스 폐렴, 또는 흡인 폐렴을 서로 확실히 감별 진단하기 어려운 때가 많다.
- 따라서 박테리아 폐렴이나 바이러스 폐렴이 아니라고 진단한 다음 역으로 흡인 폐렴이라고 진단하는 때가 더 많다.
- 사실상 신생아의 폐 속으로 태변이나 피 등이 흡인될 때 박테리아도 같이 흡인될 때가 많다.
- 따라서 박테리아 감염이 하나도 없이 순 흡인 폐렴만 생기는 경우는 아주 드물다.
- 신생아의 체온을 정상으로 유지하기 위해 보육기 속에서 치료할 때가 많다.
- 필요에 따라 산소호흡 치료를 하고, 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사로 탈수치료도 한다.
- 일반적으로 박테리아 폐렴이 아니라는 것을 확실히 알 때까지는 광범위 항생제 혈관 주사치료를 겸하는 것이 보통이다.
Aspiration pneumonia in newborn infants

Picture 160. Pneumonia chest X-ray picture Pneumonia in the upper lobe of the right lung. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
• Pneumonia caused by aspiration of amniotic fluid, maternal blood, or meconium into the airways before, during, or immediately after delivery by a fetus or newborn is called neonatal aspiration pneumonia or neonatal aspiration pneumonia. Causes of neonatal aspiration pneumonia • Newborns born with an unusually long delivery time
• Newborns born after delivery after the amniotic membrane ruptures and a long time has elapsed
• When you are born with difficulty giving birth
• When the intrauterine fetus is not getting enough oxygen and is born after sucking amniotic fluid and meconium into the lungs.
• After birth, aspiration pneumonia can also occur when the stomach contents of the newborn’s own vomit are aspirated into the airways.
• When vomit is aspirated into the airways, the aspirate and the bacteria are both sucked into the lungs and into the lungs. [Parents should also become at least the half-doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 8 Children and Adolescent Respiratory Diseases-Pleurisy, empyema, and pneumothorax.
• ⑥ Aspiration pneumonia may occur in newborns due to other causes. See Volume 8, Childhood and Adolescent Respiratory Disorders—Aspiration Pneumonia. Symptomatic Signs of Neonatal Aspiration Pneumonia

Picture 161. Suction bulb. The inhaler is mainly used to aspirate meconium, blood, and vomit from the nasal cavity, mouth, and pharynx, etc. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Picture 162. Suction catheter It is mainly used to aspirate meconium, blood, and vomit from the nasal cavity, mouth, and pharynx, etc. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• Symptoms may vary slightly depending on the amount of vomit, blood, and amniotic fluid inhaled into the lower respiratory tract and the degree of aspiration pneumonia.
• Typical symptoms of severe aspiration pneumonia include:
• Shortness of breath and pale or blue skin.
• You may even make a moaning sound when you breathe.
• There is usually no fever when there is no bacterial infection and only aspiration pneumonia.
• Bacterial infection secondary to aspiration pneumonia and fever may occur when bacterial pneumonia coexists.
• Does not suck milk or artificial nutrition well.
• These symptoms may last for several days to a week. Diagnostic treatment of neonatal aspiration pneumonia
• If this disease is suspected based on the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, diagnose by chest X-ray examination.
• In the early stages, it is often difficult to clearly differentiate between bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, or aspiration pneumonia.
• Therefore, it is more often diagnosed as not bacterial or viral pneumonia and then conversely diagnosed as aspiration pneumonia.
• In fact, when meconium or blood is sucked into the lungs of a newborn baby, bacteria are often aspirated as well.
• Therefore, it is very rare that only pure aspiration pneumonia without any bacterial infection occurs.
• Newborns are often treated in an incubator to keep their body temperature normal.
• If necessary, oxygen respiration is administered, and dehydration is also treated with intravenous glucose electrolyte solution.
• In general, it is usually combined with broad-spectrum antibiotics and intravenous injections until it is known for certain that it is not bacterial pneumonia.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Preparation for Birth. Berverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
-
Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 21st ed. Beherman,
-
The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
-
Red book 31st edition 2012
-
Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 21st Edition
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gerhon, Catherine Wilfert
-
The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
-
제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares and Diseases of Newborn Infants
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Neonatal resuscitation American academy of pediatrics
-
소아과학 대한교과서
-
그 외
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine