코 막힘, Nasal stuffing (Nasal congestion/Nasal obstruction)
|
다음은 “코가 막힘, 알레르기 비염”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q.&A. 코가 막힘, 알레르기 비염
Q.
안녕하세요. 저는 6살, 3살 아이를 둔 엄마예요. 6살 딸아이가 코가 막혀서 잠을 잘 때 힘들어해요. 그리고 숨을 쉴 수가 없는지 입으로 숨을 쉬어요. 코 속에 코가 많이 들어 있어서 그런지 그럴 때는 어떻게 해야 하는지 궁금합니다. 그 전에 병원에 가서 물어보니 코가 코 속에서 굳어서 붙어 있다하면서 코를 녹여서 빼내는데 코 속에서 피가 나더라구요. 코 속에서 코가 굳지 않게 하려면 어떡해야 하는 지도 알려주셨으면 합니다.
A.
강을님
안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다.
자녀의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답변을 드리겠습니다.
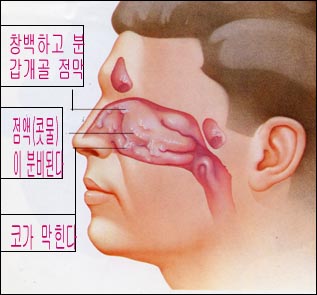
그림 92. 알레르기 비염의 대표적 증상
Used with permission from Schering Corporation Kenilworth, NJ 07033과 소아가정간호백과
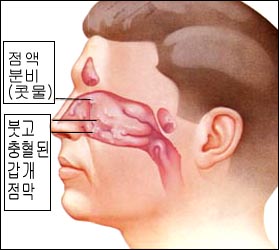
그림 163. 알레르기성 비염으로 비강 점막층이 붓고 창백하고 점액이 나오고 콧물이 나온다.
출처;Used with permission from Schering Corporation, Kenilworth, N.J. USA
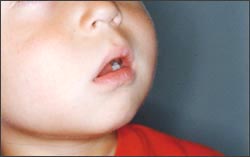
사진 95. 알레르기 비염으로 코가 막히면 입을 벌리고 입으로 숨
쉰다. 이런 호흡을 “구강호흡” 또는 “게이핑(Gaping)”이라도 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
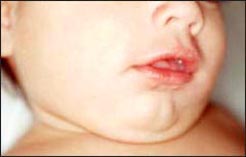
사진 96. 알레르기 비염 으로 코가 막히면 입을 벌리고 입을
통해 숨 쉰다. 이런 호흡을 구강호흡 또는 게이핑이라 한다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
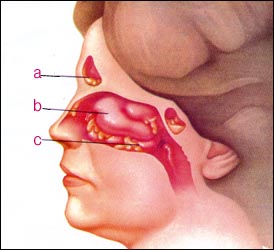
그림 109. 알레르기 비염이 있으면 부비동염에 더 잘 걸릴 수 있다.
박테리아 부비동염에 걸리면 그림에서 보는 것 같이 고름 섞인 누런 콧물이 날 수 있다.
a-고름이 잡힌 전두동 염, b-충혈이 된 비갑개, c-고름이 섞인 콧물이 날 수 있다.
Used with permission from Schering corporation, NJ, USA와 소아가장간호 백과
- 감기 등 급성 바이러스 비염
- 만성 비염,
- 위축성 비염,
- 부비동염,
- 알레르기 비염,
- 비강 내 이물,
- 선천성 코 기형,
- 후천성 코 변형,
- 아데노이드 비대,
- 비용(비 폴립),
- 약물 알레르기,
- 음식물 알레르기,
- 혈관 운동성 비염,
- 코 양성 종양
- 코 악성 종양,
- 코의 외상,
- 공해,
- 갑상선 이상 등으로 코가 막힐 수 있습니다.
- 우선 코 막힘의 원인을 알고 그 원인에 따라 치료해야 합니다.
- 비강 속에 비강 분비물(콧물)이 말라서 코가 막힐 수 있지만 그런 마른 코딱지로 코가 막혀 숨을 잘 못 쉬는 경우는 아주 드물입니다. 만일 그렇다면 그 원인을 알아 그 원인되는 기존 일차 병을 치료해야 합니다.
- 알레르기 비염이나 감기로 비강의 점막층이 부어서 코가 막힐 수 있습니다.
- 이런 때는 비강 점막 충혈 완화제로 대증치료를 할 수 있습니다.
- 경구용 2세대 항히스타민, 코르티코스테로이드제 코 분무로 치료할 수 있습니다.
- 만약 박테리아 부비동염을 의심하면 경구용 항생제로 치료해도 됩니다.
- 이런 치료는 어디까지나 의사에게 맡겨야 합니다.
- 후기 유아들이나 학령기 아이들에게 콧물이 많이 나올 때는 코를 살살 풀고 닦아도 됩니다.
- 자녀의 경우, 알레르기 비염으로 그런 코 막힘 증상 징후가 생기는 것 같습니다.
- 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단을 받으시고 그 원인에 따라서 치료해 주시기 바랍니다. 부비동염 참조.
- [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다–소아가정간호백과]-제3장 소아청소년 성장 발육–신생아 코.
- 감기.
- 제15권 소아청소년 알레르기 및 자가 면역질환–알레르기 비염을 참고하시기 바랍니다.
- 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락해 주시기 바랍니다. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Nasal stuffing (Nasal congestion/Nasal obstruction)
The following is an example of a Q&A for health counseling for children and adolescents on the Internet about “stuffy nose and allergic rhinitis”.
Q&A. stuffy nose, allergic rhinitis
Q. Good morning. I am a mother of 6 and 3-year-old children. My 6-year-old daughter has a stuffy nose and has a hard time sleeping. And she breathes through her mouth to see if she can’t breathe.
I have a lot of noise in my nose, so I wonder what to do when that happens. Before that, when I went to the hospital and asked, they said that the nose was stuck in the nose and when I melted the nose and pulled it out, the nose was bleeding.
I want you to tell me what to do to keep my nose from getting stuck in my nose.
A. Eul-nim Kang Good morning. Thanks for the nice question. The more information you know about your child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical tests, the more helpful it is to give you an answer. We will give you an answer based on the information you provided.

Figure 92. Representative symptoms of allergic rhinitis Used with permission from Schering Corporation Kenilworth, NJ 07033 and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing

Figure 163. The nasal mucosa is swollen and pale with allergic rhinitis, with mucus and runny nose. Source; Used with permission from Schering Corporation, Kenilworth, N.J. USA

Photo 95. If your nose is stuffy with allergic rhinitis, open your mouth and breathe through your mouth rest This breathing is also called “mouth breathing” or “gaping”. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Photo 96. If your nose is blocked due to allergic rhinitis, open your mouth and breathe through This breathing is called mouth breathing or gapping. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP

Figure 109. If you have allergic rhinitis, you may be more prone to sinusitis. If you get bacterial sinusitis, you may have a runny nose mixed with pus as shown in the picture. A – frontal sinusitis with pus, b – congested turbinate, c – runny nose mixed with pus. Used with permission from Schering Corporation, NJ, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric Parenting Nursing
• Acute viral rhinitis such as a cold
• chronic rhinitis;
• atrophic rhinitis;
• Sinusitis;
• allergic rhinitis;
• foreign body in the nasal cavity;
• Congenital anomalies of the nose;
• Acquired nasal deformity;
• Adenoid hypertrophy,
• cost (non-polyps);
• drug allergies;
• food allergies;
• vasomotor rhinitis,
• Nasal benign tumors
• nasal malignancies;
• trauma to the nose;
• Pollution,
• Your nose may be blocked due to abnormalities in the thyroid gland, etc.
• First, you need to know the cause of the stuffy nose and treat it according to the cause.
• Nasal secretions (runny nose) in the nasal passages can dry out and cause a stuffy nose, but it is very rare for such dry snot to make breathing difficult. If so, you need to find out the cause and treat the existing primary disease that is causing it.
• Allergic rhinitis or a cold can cause the nasal mucosa to swell and become stuffy.
• In this case, nasal mucosal decongestants can be used as symptomatic treatment.
• Can be treated with oral second-generation antihistamines, corticosteroids and nasal sprays.
• If bacterial sinusitis is suspected, it may be treated with oral antibiotics.
• This treatment should be left to your doctor.
• If you have a runny nose in late infants or school-age children, you can gently blow and wipe your nose.
• In your child, allergic rhinitis seems to be causing these signs of a stuffy nose.
• Please receive a diagnosis from the Department of Pediatrics and treat it according to the cause. See Sinusitis.
• [Parents should also become anti-doctors – Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing] – Chapter 3 Growth and Development of Children and Adolescents – Newborn Nose.
• cold.
• Please refer to Volume 15 Allergy and Autoimmune Diseases in Children and Adolescents – Allergic Rhinitis.
• If you have more questions, please feel free to contact us. Thank you. Lee Sang-won Lee.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
-
Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
-
The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
-
Breastfeeding by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- 제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환 참조문헌 및 출처
-
Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
-
Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
-
Emergency care, Harvey grant, and Robert Murray
-
Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
-
Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
-
Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
-
Neonatal resuscitation American academy of pediatrics
-
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.