척주 측만증(척추 옆굽음증), Scoliosis
척주 측만곡증(척주 측만증)의 원인
- 척주에 생리적으로 경추 만곡, 흉추 만곡, 요추 만곡 그리고 골반 만곡이 약간 있는 것이 정상적이다.
- 척주의 일부분이 비정상적으로 좌측이나 우측으로 만곡된 상태를 척주 측만이라 한다.
- 척주 측만으로 생기는 증상 징후를 척주 측만증 또는 척주 측만곡증이라 한다.
- 학령기 아이들에게 척주 측만증이 생기는 빈도는 거의 10%이다.
- 그 중 약 60~80%는 특발성 척주 측만증이다.
- 척주 측만증에는 선천성으로 생기는 선천성 척주 측만증과 후천성으로 생기는 후천성 척주 측만증이 있다.
- 원인을 확실히 알 수 없이 생기는 원발성 척주 측만증(특발성 척주 측만증),
- 근육신경 이상 등으로 생기는 근육신경 이상 척주 측만증도 있다.
- 평소에 자세를 바르게 취하지 않아 생기는 척주 측만증,
- 척주염이나 척주외상이나 척주 종양 등으로 척주가 비정상으로 좌측이나 우측으로 조금 만곡된 척주 측만증도 있다.
- 원발성 척주 측만증은 생후 어느 때든지 생길 수 있지만 사춘기가 시작되기 바로 전 부터 더 잘 생길 수 있고
- 여아의 경우 11세경, 남아의 경우 12~14 경에 현저하게 나타나는 것이 보통이다.
- 즉 사춘기가 시작하기 전 약간 만곡되어 있던 척주가 사춘기가 오기 시작하면서 척주 만곡이 불과 1~2년 동안 현저하게 심하게 만곡되어 척주 측만의 중증도가 뚜렷하게 나타날 수 있고 증상 징후도 생길 수 있다.
- 뇌성마비, 소아마비, 척수수막류, 프리드라히 운동실조, 척수외상, 신경 섬유증, 마르팡증, 엘러스단로스증, 척수종양, 척주골종, 구루병, 불완전 골형성증, 비타민 A과다증, 갑상선 기능저하증, 연소성 류마토이드 관절염, 뮤코다당체 침착증 (점다당질증), 척주염, 척주결핵 등으로 척주 측만증이 생길 수 있다.
- 척주 측만증, 척주 후만증, 누두흉 등은 호흡기에 관련된 정형외과 질환이다.
척주 측만곡증(척주 측만증)의 증상 징후
- 척주 측만증을 일으킨 원인과 정도에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
- 이론적으로 척주의 어느 부위에도 생길 수 있다.
- 흉부 척주에만 생길 수도 있고 흉부 척주의 일부와 허리 척주(흉요부 척주)의 일부에만 생길 수도 있고, 어떤 때는 허리 척주(요부 척주)에만 생길 수 있다.
- 척주 측만이 생긴 척주 부위가 좌측으로 또는 우측으로 경미하게 만곡 될 수 있고, 또는 심하게 만곡 될 수 있다.
- 척주 측만의 정도가 심하지 않을 때는 척주가 조금 측만 되었을 뿐 아무런 다른 증상 징후가 나타나지 않는다.
- 척주 측만이 심하게 생겼을 때는 외관상으로 척주 측만이 있는 것을 쉽게 알 수 있다, 사진 129~130참조.
- 더 심하면 옷을 입고 있는 상태에서도 척주가 측만 된 것이 겉으로 나타나고 평소에 운동을 자유자재로 할 수 없다.
- 심한 척주 측만을 적절히 치료해 주지 않으면 흉강 구조에도 변화가 생겨서 호흡 곤란이 생길 수 있고 수명이 더 짧아진다.
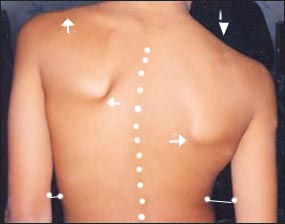
사진 129. 척주 측만.
하얀 점선으로 표시된 선과 같이 척주가 측만되어 있다. 팔과 허리 사이의 간격에 차이가 난다. 양쪽 어깨 높이에 차이가 난다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
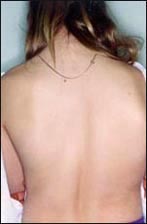
사진 130. 척주 측만이 되어 있다. 사춘기 여아의 후면 등 사진
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
척주 측만곡증(척주 측만증)의 진단
- 척주 측만증의 중증도에 따라 경증, 중등증, 중증의 척주 측만증으로 구분한다.
- 병력, 증상 징후와 진찰소견 등을 종합해 척주가 측만 되어 있다고 의심되면 척추측만계로 척주 측만의 정도를 재보고 필요에 따라 척주 X선 사진 검사로 확진한다.
- 경증 척주 측만이 있는 유아들, 학령기 아이들, 사춘기 아이들이 옷을 입고 있을 때는 이 병이 있는지 쉽게 알 수 없다.
- 겉옷을 벗고 반듯이 서 있을 때 머리끝에서 엉덩이까지 척주 전체를 살펴보면 척주의 일부가 우측 옆으로 또는 좌측 옆으로 휘어지고
- 한쪽 어깨의 높이가 다른 쪽 어깨 높이보다 더 낮다.
- 한쪽 앞가슴이 다른 쪽 앞가슴보다 앞으로 더 불쑥 나와 있다.
- 반듯이 서서 두 팔을 양쪽 옆구리로 반듯이 내려 양 옆 몸통에 붙일 때 한쪽 옆구리와 그쪽 팔 사이의 간격이 반대쪽의 사이 간격보다 더 많이 벌어져서 양쪽 옆구리와 팔 사이의 간격이 다르다(사진 129 참조).
- 척추측만계로 척주 만곡의 정도를 쟀을 때 척주가 6~7도 이상 만곡 되면 척주 만곡이 확실히 있는 것으로 진단한다.
- 마지막으로 척주 X선 사진 검사로 척주 측만의 정도를 더 확실히 알아보고,
- 또 육체적 운동, 물리치료, 브레이스, 수술로 치료해야 하는지 알아본다.

사진 132. 척추 측만곡의 정도를 재는 기구
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
척주 측만곡증(척주 측만증)의 치료
- 정도에 따라 다르게 치료한다.
- 경증 척주 측만이 있을 때는 자신도 부모도 자녀가 그 병을 가졌는지 잘 알지 못할 때가 많다. 경증 척주 측만이 불과 몇 달 동안에 중증 척주 측만으로 변화할 수 있다.
- 소아청소년 정기 건강검진을 받을 때마다 척주 측만이 있는지 기본적으로 진찰해서 알아야 한다.
- 경증 척주 측만을 조기에 진단해서 더 이상 악화되지 않도록 조기에 적절히 치료해야 한다.
- 경증 척주 측만은 적절한 운동과 물리치료 등으로 치료한다.
- 경증 척주 측만을 처음으로 진단 받은 후 부터 적어도 만 18세가 될 때까지 더 악화되는지 주기적으로 추적 진찰을 받고 필요에 따라 적절한 치료도 받아야 한다.
- 경증 척주 측만이 짧은 기간 동안에 더 악화되어 중등도 척주 측만이나 중증 척주 측만으로 될 수 있다.
- 그때그때 척주 측만의 진행 정도에 따라 운동, 물리치료, 찰스톤(Charleston) 브레이스 등으로 적기에 적절히 치료 받아야 한다. 이렇게 해서 될 수 있는 한 수술치료를 피해야 한다.
- 중증 척주 측만은 밀와키 브레이스 또는 척수 수술 등으로 치료한다.
- 브레이스 치료를 해줄 때는 목 부위에서부터 엉덩이 부위까지 걸치는 브레이스로 2~4년간 밤낮으로 치료하든지 또는 찰스톤(Charleston) 브레이스로 낮에만 치료할 수 있다.
- 선천성 척주 측만은 3~4세에 수술로 치료할 수 있고
- 근육신경성 척주 측만증은 브레이스 치료로 잘 치료되지 않고 수술로 치료하는 것이 일반적이다. 오랫동안 이런 치료를 받을 때 육체적으로 정신적으로 큰 부담이 될 수 있다.
- 그러므로 척주 측만은 조기에 진단하여 가능한 한 운동치료나 물리치료 등으로 보다 더 쉽고 덜 고생하면서 치료받아야 한다.
- 즉 브레이스 치료나 척수 수술로 치료받아야 할 때까지 척주 측만증이 진행되지 않도록 최대한으로 노력해야 한다.
- 중기나 후기의 사춘기 아이들에 생기는 특발성 척주 측만증의 예후는 일반적으로 좋다.
- 척추 측만증의 증증도에 따라, 척주 측만증을 치료할 때 쓰는 브레이스로 인해 호흡 곤란도 생길 수 있다.
- 이런 측만 척주증을 치료할 때 쓰는 브레이스로 호흡기 기능에 많은 제한이 생길 수 있다.
Scoliosis (curvature of the spine)
Causes of scoliosis
• It is normal for the spine to have physiological cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and slight pelvic curvature.
• A condition in which a part of the spine is abnormally curved to the left or right is called scoliosis.
• Symptomatic signs of scoliosis are called scoliosis or scoliosis.
• The incidence of scoliosis in school-age children is nearly 10%.
• About 60-80% of them are idiopathic scoliosis.
• Scoliosis includes congenital scoliosis and acquired scoliosis.
• primary scoliosis of unknown cause (idiopathic scoliosis);
• There is also scoliosis, which is caused by muscular nerve abnormalities such as muscular nerve abnormalities.
• Scoliosis caused by improper posture,
• There is also scoliosis, in which the spine is slightly curved to the left or right due to spondylitis, spinal trauma, or tumor.
• Primary scoliosis can develop at any time after birth, but is more likely just before the onset of puberty and
• It is usually noticeable around the age of 11 in girls and around 12-14 in boys.
• In other words, the spinal column, which was slightly curved before the onset of puberty, becomes significantly more curved for only 1 to 2 years as puberty begins, so the severity of scoliosis can be clearly seen and symptomatic signs can occur.
• Cerebral palsy, polio, meninges, Friedrich’s ataxia, spinal cord trauma, neurofibromas, spinal tumor, osteosarcoma, rickets, osteogenesis imperfecta, hypervitaminosis A, hypothyroidism, Scoliosis can be caused by juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, mucopolysaccharide deposition (point polysaccharidosis), spondylitis, and spinal tuberculosis. 뇌성마비, 소아마비, 척수수막류, 프리드라히 운동실조, 척수외상, 신경 섬유증, 마르팡증, 엘러스단로스증, 척수종양, 척주골종, 구루병, 불완전 골형성
• Scoliosis, kyphosis, and pectoralis minor are orthopedic diseases related to the respiratory system.
Signs, symptoms of scoliosis
• Symptoms vary depending on the cause and severity of scoliosis.
• Theoretically, it can occur anywhere in the spine.
• It may occur only on the thoracic spine, on only part of the thoracic spine and on parts of the lumbar spine (thorax-lumbar spine), and sometimes only on the lumbar spine (lumbar spine).
• The area of the spinal column with scoliosis may be slightly curved to the left or right, or it may be severely curved.
• When the degree of scoliosis is not severe, there is only a slight scoliosis and no other symptoms appear.
• When the scoliosis is severe, it is easy to tell that there is a scoliosis visually, see pictures 129~130.
• In more severe cases, a scoliosis of the spine appears apparent even when wearing clothes, and you cannot exercise freely.
• If severe scoliosis is not properly treated, changes in the structure of the chest cavity can lead to breathing difficulties and a shorter lifespan.

Photo 129. Scoliosis of the spine.
As shown by the white dotted line, the spinal column is scoliosis. There is a difference in the distance between the arm and the waist. There is a difference in the height of both shoulders. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP Picture

130. Only the vertebral column is shown. Back photo of a teenage girl Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Diagnosis of scoliosis
• According to the severity of scoliosis, it is divided into mild, moderate and severe scoliosis.
• If it is suspected that the spinal column is scoliosis based on the medical history, symptom signs, and examination findings, the degree of scoliosis is reassessed with a scoliometer and, if necessary, confirmed by X-ray examination of the spinal column
. • Infants with mild scoliosis, school-age children, and adolescents cannot easily tell if they have the disease when they are wearing clothes.
• When you take off your outerwear and stand up straight, if you look at the entire spinal column from the top of your head to your buttocks, you can see that part of the spinal column is curved to the right or left
• One shoulder is lower than the other.
• One pronotum protrudes more forward than the other pronotum.
• When standing upright and lowering both arms to both sides of the body and attaching them to the body, the gap between one side and the other arm is wider than the gap between the other side, so the distance between both sides of the arm is different (refer to photo 129).
• When the degree of curvature of the spinal column is measured with a scoliometer, if the spinal column is curved more than 6-7 degrees, it is diagnosed that there is a definite spinal curvature. • Finally, a spinal x-ray examination to determine the degree of scoliosis more clearly,
• Also find out if you need to be treated with physical exercise, physical therapy, braces, or surgery.

Picture 132. Instrument to measure the degree of scoliosis Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, M.D., FAAP
Treatment of scoliosis
• Treat differently depending on the severity.
• When there is mild scoliosis, neither you nor your parents are aware that your child has the disease. A mild scoliosis can turn into a severe scoliosis in just a few months.
• Whenever children and adolescents receive regular health check-ups, they should basically examine and find out if there is a scoliosis.
• Mild scoliosis should be diagnosed at an early stage and treated appropriately to prevent further deterioration.
• Mild scoliosis is treated with appropriate exercise and physical therapy.
• From the first diagnosis of mild scoliosis until at least the age of 18, follow-up should be performed periodically to see if the condition worsens, and appropriate treatment should be provided if necessary.
• Mild scoliosis can get worse over a short period of time, leading to moderate or severe scoliosis.
• Depending on the degree of progress of scoliosis from time to time, appropriate treatment with exercise, physical therapy, and Charleston braces should be performed in a timely manner. In this way, surgical treatment should be avoided as far as possible.
• Severe scoliosis can be treated with a Milwaukee brace or spinal cord surgery.
• When giving brace treatment, it can be treated day and night for 2 to 4 years with a brace that extends from the neck to the buttocks, or it can be treated only during the day with a Charleston brace.
• Congenital scoliosis can be treated surgically at 3 or 4 years of age.
• Musculoskeletal scoliosis is not treated well with braces and is usually treated with surgery. It can be a huge burden physically and mentally when undergoing such treatment for a long time.
• Therefore, scoliosis should be diagnosed at an early stage and treated with exercise or physical therapy as much easier and less pain as possible.
• You should do your best to prevent scoliosis from progressing until you need to be treated with braces or spinal surgery.
• The prognosis for idiopathic scoliosis in middle or late puberty is generally good.
• Depending on the severity of scoliosis, the braces used to treat scoliosis may also cause breathing difficulties.
• The brace used to treat this type of scoliosis can limit respiratory function.
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.