신생아 폐렴, Neonatal pneumonia(Pneumonia of newborn infants/Pneumonia in newborn
다음 정보를 참조(Please visit the following article) www.drleepediatrics.com-제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 제 2부 신체각계통 별 응급의료 제7장: 소아청소년 호흡기 질환 응급의료 참조
Please visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System-Chapter 7: child adolescents respiratory Disease Emergency Medical care
| 신생아 폐렴의 원인 |
- 신생아에게 생기는 폐렴을 신생아 폐렴, Neonatal pneumonia, Pneumonia of newborns, 또는 Pneumonia in newborns 이라 한다.
- 임신부에게 감염됐던 박테리아나 바이러스 등의 병원체가 태반을 통과하여 태아에게 감염되면 태아가 선천성 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다. 태어난 후 신생아 폐렴을 진단 받을 수 있다.
- 분만 중, 질 산도에서 세균을 기도 내로 흡인할 때 세균이 폐 속으로 감염될 수 있고
- 신체 다른 계통의 국소 감염병 병소에 있던 세균이 혈류를 따라 전신으로 퍼져 신생아 폐 속으로 감염될 수 있고,
- 때로는 호흡할 때 세균을 흡입해서 폐에 감염되어 신생아 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
| 신생아 폐렴의 분류 |
1. 선천성 신생아 폐렴
- 임신부에게 감염됐던 박테리아나 바이러스 등의 병원체가 태반을 통과하여 태아에게 감염되면 태아가 선천성 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 이처럼 출생하기 전 태아가 걸린 폐렴을 선천성 폐렴이라고 한다.
- 선천성 폐렴이 있는 신생아의 폐렴을 선천성 신생아 폐렴이라고 한다.
2. 후천성 신생아 폐렴
- 분만 중 태어나는 아기가 박테리아에 감염된 양수, 모체의 분비물, 엄마의 피, 태변 등이 아기의 기도 속으로 흡인된 후 태어난 신생아에게 흡인 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
- 불결한 주위에 있던 병원체가 신생아의 폐에 감염될 때 후천성 신생아 폐렴에 걸릴 수도 있다.
| 원인 병원체의 종류에 따라 신생아 폐렴 분류. |
1. 박테리아(박테리아) 신생아 폐렴
- 대장균,
- B군 용혈성 연쇄상구균,
- 슈도모나스균(녹농균),
- 푸로테우스균,
- 황색 포도상구균,
- 매독균 또는
- 그외 다른 여러 종류의 박테리아 감염으로 박테리아 신생아 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
2. 바이러스 신생아 폐렴
- 사이토메갈로바이러스,
- 풍진 바이러스 등 여러 종류의 바이러스 감염으로 바이러스 신생아 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
3. 주폐포자충 폐렴 Pneumonia due to Pneunocystis carinii
주폐포자충 감염으로 신생아 주폐포자충 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
4. 흡인 신생아 폐렴 Neonatal pneumonia due to aspiration
- 분만 중 양수, 모체의 피, 또는 변, 아기 자신이 본 태변 등을 기도 속으로 흡인해서 흡인 신생아 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 출생 후 모유, 인공영양, 구토 물 등을 폐 속으로 흡인해 흡인 신생아 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
5. 2차 박테리아 감염으로 생기는 신생아 폐렴 Pneumonia due to secondary
bacterial infections
- 다른 병을 앓을 때 합병증으로 신생아 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
- 예를 들면, 중이염이나 바이러스 상기도 감염병을 앓을 때 그 병의 합병증으로 이차 박테리아 폐렴에 걸릴 수 있다.
- 패혈증이나 뇌막염을 앓을 때 그 병을 일으킨 세균이 폐에 감염되어 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
6. 진균 감염으로 생기는 신생아 폐렴 Pneumonia due to Fungal infection
곰팡이(진균)에 신생아 폐가 감염되면 신생아 진균 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
7. 마이코플라스마 감염( 미코플라스마 감염)으로 생기는 신생아 폐렴
마이코플라스마 균에 신생아 폐가 감염되면 신생아 마이코플라스마 균 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
8. 톡소프라스마 원충 감염으로 생기는 신생아 폐렴
톡소프라스마 원충에 태아의 폐나 신생아의 폐가 감염되면 신생아 톡소프라스마 원충 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
9. 클라미디아 감염으로 생기는 신생아 폐렴
클라미디아에 신생아 폐가 감염되면 신생아 클라미디아 폐렴이 생길 수 있다.
클라미디아 감염과 폐렴, [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과]-제19권 소아청소년 안과 질환-클라미디아 결막염 참조.
10. 그 외 원인으로 생기는 신생아 폐렴
| 신생아 폐렴의 증상 징후 |
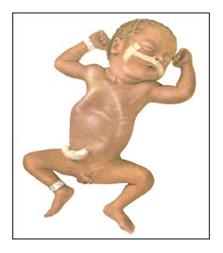
사진 159. 흉골 함몰(Sternal retraction)
심한 폐렴을 앓을 때 흉골이 숨 쉴 때마다 함몰될 수 있다.
출처: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA와 소아가정간호백과
신생아 폐렴이 태어나기 전 자궁 내에서, 분만 중, 분만 후 어느 때 생겼는지에 따라, 폐렴을 일으킨 원인, 폐렴을 일으킨 세균의 종류, 합병증의 유무 등에 따라 증상 징후가 다르다.
전형적인 박테리아(박테리아) 신생아 폐렴의 증상 징후는 다음과 같다.
- 출생 이전 태아기에 걸린 신생아 폐렴이나 분만 중 걸린 신생아 폐렴이 있는 신생아는 출생 직후부터 어딘가가 아픈 것 같이 보인다.
- 모유나 인공영양을 잘 빨아먹지 못 한다.
- 비정상적으로 잠을 많이 자거나
- 힘없이 축 늘어질 수 있다.
- 고열이 나기도 하고, 고열이나 미열이 나는 대신 오히려 체온이 정상 이하로 떨어지고 저체온이 생길 수 있고 몸이 찰 수 있다.
- 구토와 설사를 할 수 있다.
- 신생아나 영아가 심한 폐렴에 걸려 숨을 제대로 쉬지 못할 때는 사진 159에서 보는 것같이 흉골과 흉골 검상돌기 등이 흉곽강 속으로 숨을 쉬는 대로 함몰되어 끌려 들어갔다 나왔다 할 수 있다.
- 그리고 복벽도 숨 쉴 때 함몰되기도 한다.
- 이렇게 흉골이나 복벽 등이 숨 쉴 때마다 함몰되면 심한 호흡곤란이 있다는 것을 의미한다. 의사의 진단 치료가 긴급하게 요한다.
- 콧날개(비익)가 숨 쉴 때마다 벌렁 벌렁거리고 신음소리를 내면서 숨 쉬고 피부가 창백하고 잘 먹지 않는 증상이 흉골 함몰 증상과 같이 있을 때는 생명에 상당히 위험스러운 상태에 있는 신생아이다.
- 숨을 빠르게 쉬고 호흡곤란이 생길 수도 있고 무호흡증이 생기거나 불규칙하게 호흡하기도 한다.
- 피부가 창백해지고 푸르스름해질 수 있다.
- 그러나 기침은 거의 하지 않는다.
- 신체의 움직임이 과다하고 근육이 이완되고 팔다리에 진전이 생길 수 있다.
- 때로는 전신 발작도 한다.
- 이런 증상 징후 이외에 폐렴으로 생긴 합병증에 의한 증상 징후가 같이 나타날 수 있다.
| 신생아 폐렴의 진단과 치료 |
- 병력, 증상, 진찰소견 등을 종합해서 폐렴이 의심되면 피와 소변, 대변, 뇌척수액 검사 등을 하고, 가슴 X선 사진 등으로 진단한다.
- 피, 가래, 뇌척수액, 소변, 대변 등에서 채취한 피검물로 세균 배양검사를 하여 어떤 세균이 폐렴을 일으켰나 알아본다.
- 신생아가 박테리아 폐렴에 걸렸을 때는 즉시 병원 신생아 집중 치료실에 입원하여 포도당 전해질용액 정맥주사와 광범위 항생제혈관 주사로 응급하게 치료를 시작한다.
- 필요하면 산소 호흡치료를 한다.
- 원인되는 세균의 종류에 따라 또는 항균제 감수성 검사로 알아낸 적절한 항생제 주사로 치료한다.
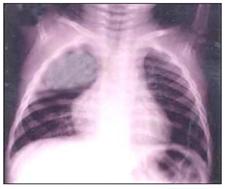
사진 160. 폐렴이 가슴 X선 사진.
우측 폐의 상엽에 폐렴이 있다.
출처-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Neonatal pneumonia (Pneumonia of newborn infants/Pneumonia in newborn)
Please visit the following article: www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System See Chapter 7: Emergency Medical Care for Respiratory Disorders in Children and Adolescents Please visit www.drleepediatrics.com-Volume 1 Emergency Medical Care for Children and Adolescents Part 2 Emergency Medical Care for Each System-Chapter 7: child adolescents respiratory Disease Emergency Medical care Causes of neonatal pneumonia • Pneumonia that occurs in newborns is called neonatal pneumonia, Pneumonia of newborns, or Pneumonia in newborns.
• If pathogens such as bacteria or viruses that have been infected by a pregnant woman pass through the placenta and infect the fetus, the fetus may contract congenital pneumonia. Neonatal pneumonia can be diagnosed after birth.
• During labor, when bacteria are aspirated into the airways from the vaginal acid canal, bacteria can enter the lungs and
• Bacteria from local infectious disease lesions in other systems of the body can spread throughout the body through the bloodstream and infect the newborn’s lungs;
• Sometimes breathing in bacteria can infect the lungs and cause neonatal pneumonia. Classification of neonatal pneumonia 1. Congenital neonatal pneumonia
• If pathogens such as bacteria or viruses that have been infected by a pregnant woman pass through the placenta and infect the fetus, the fetus may contract congenital pneumonia.
• Pneumonia acquired by the fetus before birth is called congenital pneumonia. • Pneumonia in newborns with congenital pneumonia is called congenital neonatal pneumonia.
2. Acquired neonatal pneumonia
• Aspiration pneumonia may occur in newborns born after a baby born during labor is aspirated into the baby’s airways with bacteria-infected amniotic fluid, maternal secretions, mother’s blood, and meconium.
• Acquired neonatal pneumonia can occur when pathogens from unclean surroundings infect the newborn’s lungs. Classification of neonatal pneumonia according to the type of causative agent.
1. Bacterial (bacterial) neonatal pneumonia
• E. coli;
• group B hemolytic streptococci;
• Pseudomonas (Pseudomonas aeruginosa),
• Proteus,
• Staphylococcus aureus;
• Syphilis or
• Many other bacterial infections can cause bacterial neonatal pneumonia.
2. Virus neonatal pneumonia
• cytomegalovirus;
• Viral neonatal pneumonia can be caused by several types of viral infection, such as the rubella virus.
3. Pneumonia due to Pneunocystis carinii Pneumocystis pneumonia in newborns can result from Pneumocystis pneumonia infection.
4. Neonatal pneumonia due to aspiration
• During delivery, amniotic fluid, mother’s blood or feces, or meconium seen by the baby can be aspirated into the airways and cause aspiration pneumonia in newborns.
• After birth, aspiration of breast milk, artificial nutrition, or vomit into the lungs can cause aspiration pneumonia in newborns.
5. Pneumonia due to secondary bacterial infection bacterial infections
• Neonatal pneumonia may occur as a complication when suffering from other illnesses.
• For example, when you have otitis media or a viral upper respiratory tract infection, you can get secondary bacterial pneumonia as a complication of the disease.
• When you have sepsis or meningitis, the bacteria that caused the disease can infect your lungs and cause pneumonia.
6. Pneumonia due to Fungal infection Fungal infection of the newborn lungs can cause neonatal fungal pneumonia.
7. Neonatal pneumonia caused by mycoplasma infection (mycoplasma infection) Neonatal lung infection with Mycoplasma bacteria can cause neonatal Mycoplasma pneumonia.
8. Neonatal pneumonia caused by Toxoplasma protozoa infection Toxoplasma protozoa can infect the lungs of a fetus or the lungs of a newborn, resulting in neonatal Toxoplasma pneumoniae.
9. Neonatal pneumonia due to chlamydial infection Chlamydia can cause neonatal chlamydial pneumonia if it infects the newborn’s lungs. Chlamydia Infection and Pneumonia, [Parents Should Be Anti-Doctors-Children and Family Nursing Encyclopedia]-Volume 19 Ophthalmic Diseases in Children and Adolescents-Chlamydia Conjunctivitis.
10. Neonatal pneumonia caused by other causes Symptoms Signs of Pneumonia in Newborns

Picture 159. Sternal retraction In severe pneumonia, the sternum may retract with every breath. Source: Used with permission from Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing Symptoms and signs of neonatal pneumonia vary depending on whether it occurred in the uterus before, during, or after delivery, the cause of the pneumonia, the type of bacteria that caused the pneumonia, and the presence or absence of complications.
Symptoms of typical bacterial (bacterial) neonatal pneumonia include:
• Newborns with neonatal pneumonia from the prenatal period or neonatal pneumonia from birth before birth appear to be ill somewhere soon after birth.
• I am not able to suck up breast milk or artificial nutrition well.
• Sleeping abnormally or
• Can droop without force.
• You may have a high fever, and instead of having a high or low fever, your body temperature may drop below normal, and hypothermia may occur and the body may become full.
• May cause vomiting and diarrhea.
• When a newborn or infant has severe pneumonia and cannot breathe properly, as shown in photo 159, the sternum and xiphoid process can be pulled into and out of the thoracic cavity as they breathe.
• And the abdominal wall also collapses when breathing.
• If the sternum or abdominal wall collapses every time you breathe, it means that you have severe breathing difficulties. Diagnostic treatment by a doctor is urgently needed.
• A newborn baby is in a very life-threatening condition when the nostrils (fins) are flapping and moaning with every breath, pale skin, and difficulty eating together with the symptoms of depression of the sternum.
• Breathing quickly and you may have trouble breathing, have apnea or have irregular breathing.
• Your skin may turn pale and bluish.
• But seldom cough.
• Excessive body movement, muscle relaxation, and tremors in the limbs may occur.
• Sometimes even generalized.
• In addition to these symptomatic signs, symptoms of complications caused by pneumonia may also appear.
Diagnosis and treatment of neonatal pneumonia
• If pneumonia is suspected by combining the medical history, symptoms, and examination findings, blood, urine, stool, and cerebrospinal fluid tests are performed, and a chest X-ray is used for diagnosis.
• Check which bacteria caused pneumonia by performing a bacterial culture test with specimens collected from blood, sputum, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and feces.
• When a newborn develops bacterial pneumonia, immediately enter the hospital’s neonatal intensive care unit and begin emergency treatment with intravenous glucose electrolyte solution and intravenous broad-spectrum antibiotic injection.
• Administer oxygen breathing therapy if necessary.
• Treat with appropriate antibiotic injections determined by the antimicrobial susceptibility test or according to the type of causative bacteria.

Picture 160. Pneumonia chest X-ray. Pneumonia in the upper lobe of the right lung. Source-Copyrightⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine